Solutions
Products
-
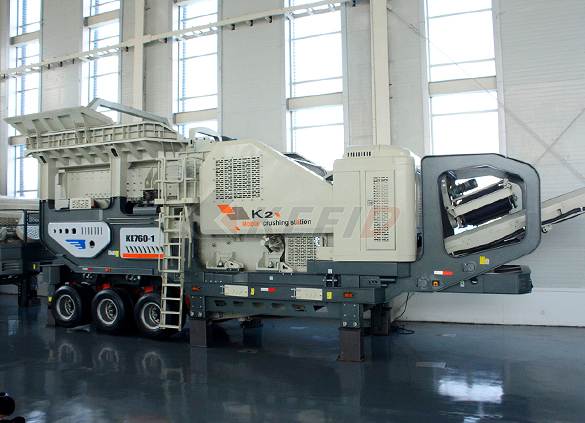

Primary mobile crushing plant
-
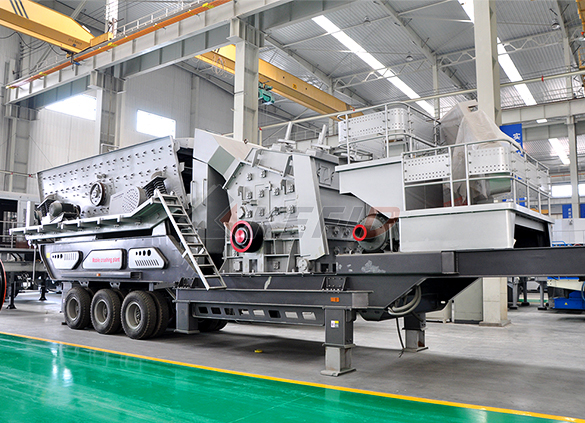

Independent operating combined mobile crushing station
-
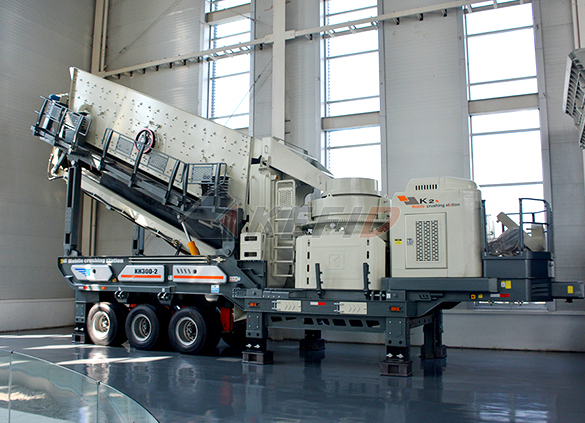

Mobile secondary crushing plant
-
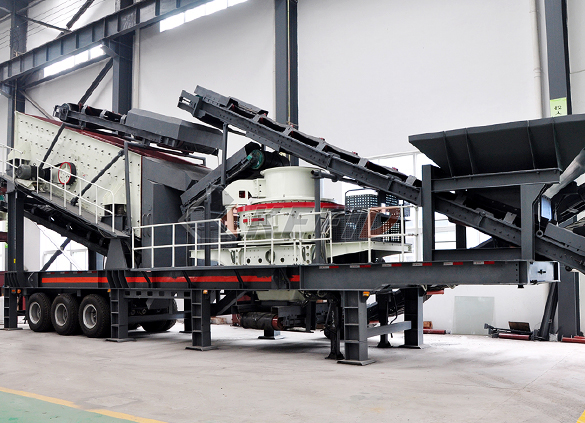

Fine crushing and screening mobile station
-
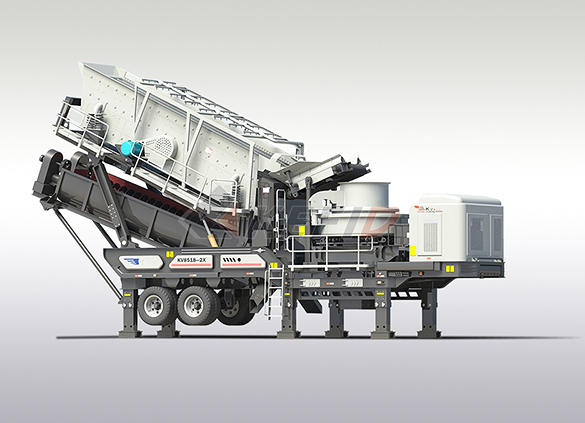

Fine crushing & washing mobile station
-
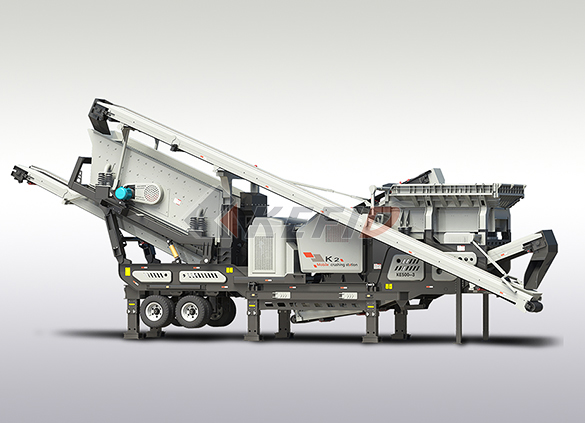

Three combinations mobile crushing plant
-
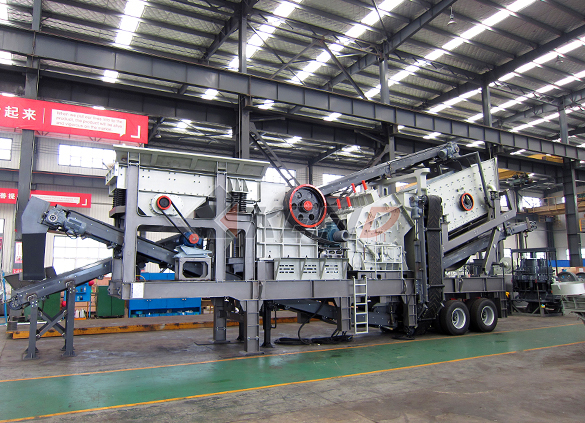

Four combinations mobile crushing plant
-
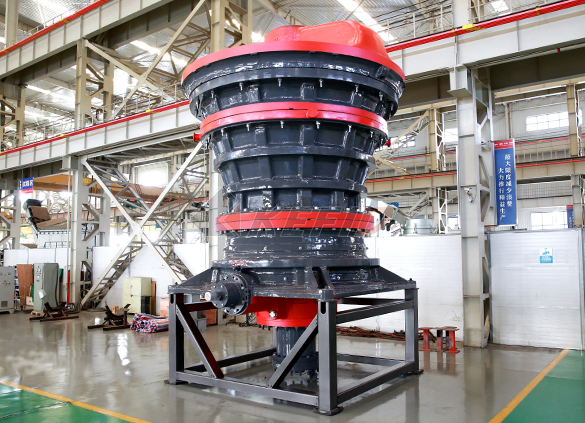

HGT gyratory crusher
-
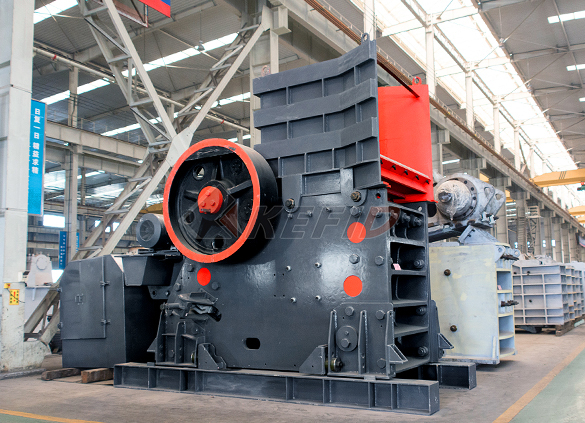

C6X series jaw crusher
-
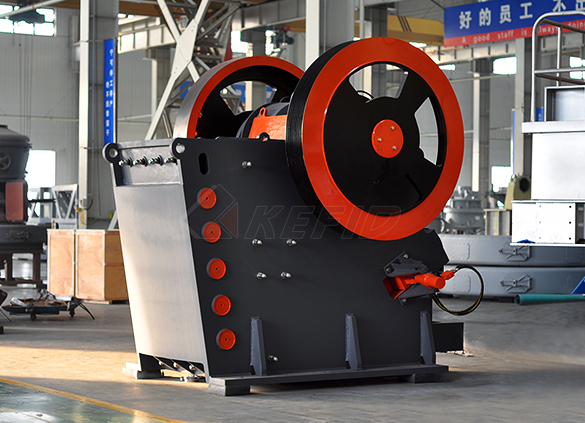

JC series jaw crusher
-
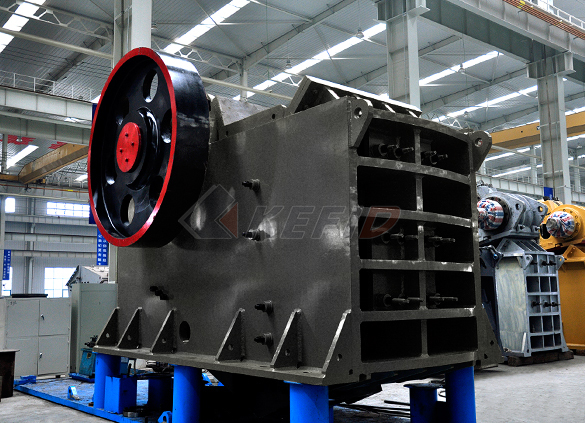

Jaw crusher
-
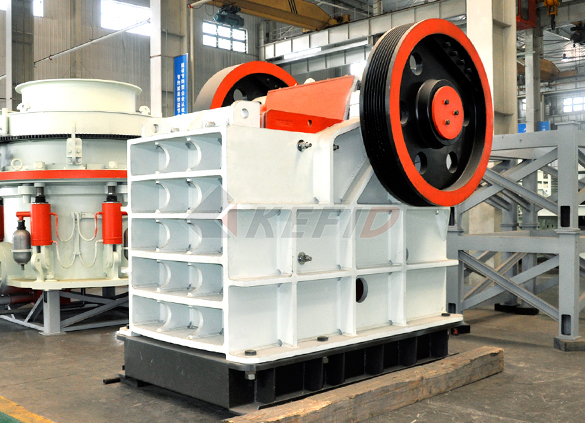

HJ series jaw crusher
-
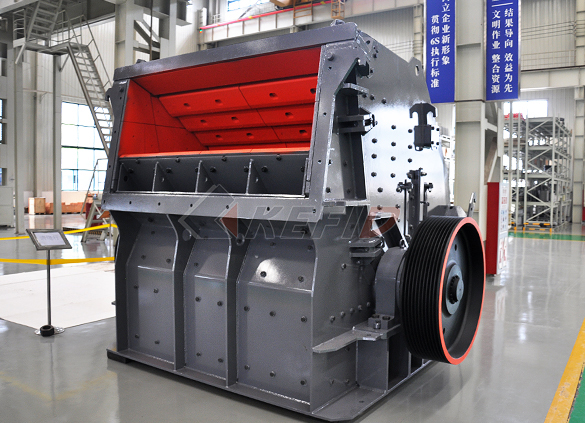

CI5X series impact crusher
-
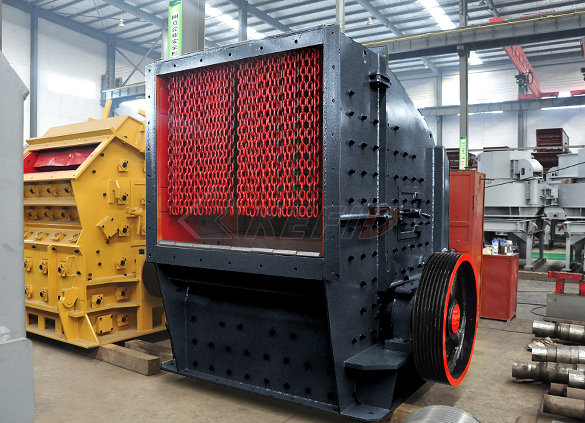

Primary impact crusher
-
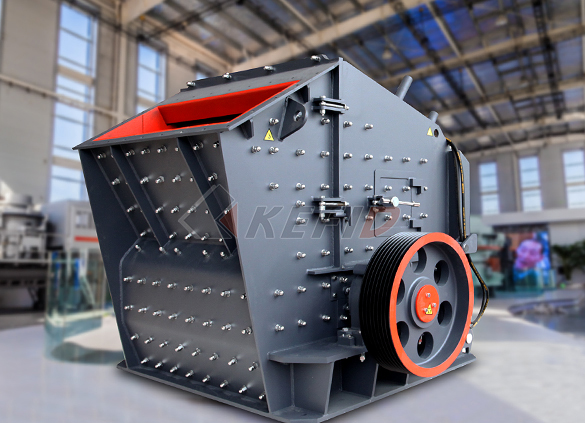

Secondary impact crusher
-
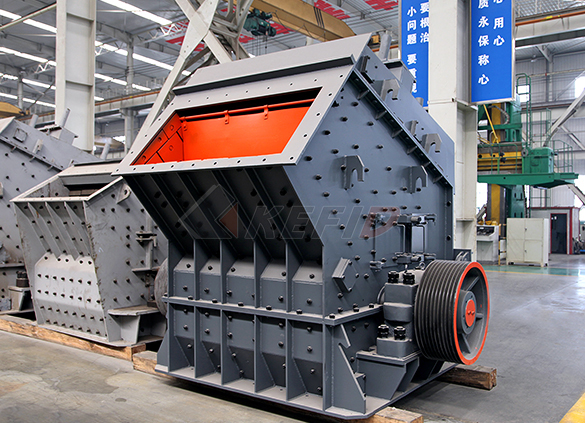

Impact crusher
-
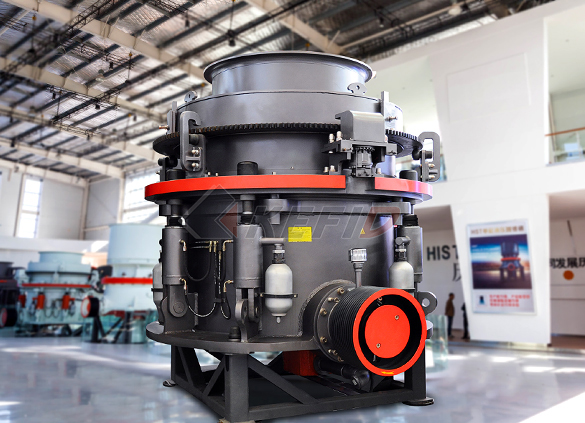

HPT series hydraulic cone crusher
-
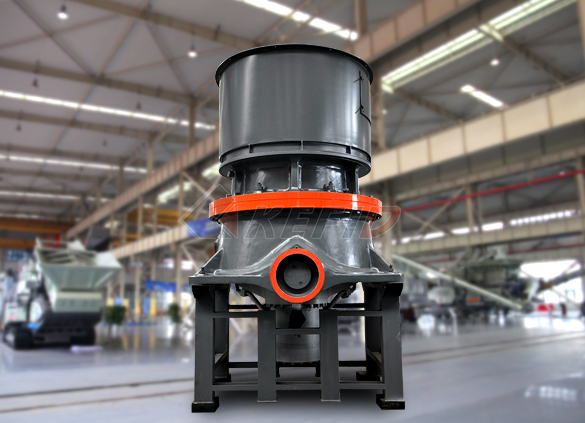

HST hydraulic cone crusher
-
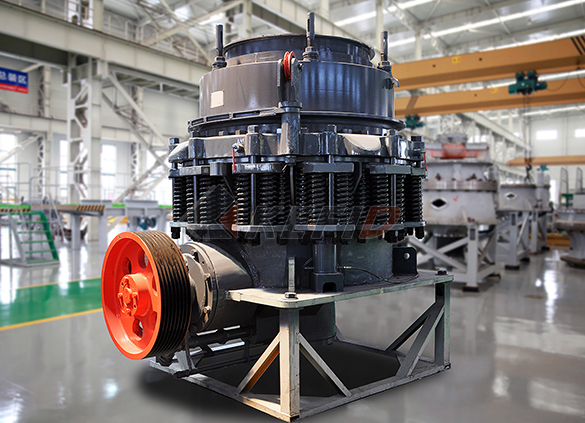

CS cone crusher
-
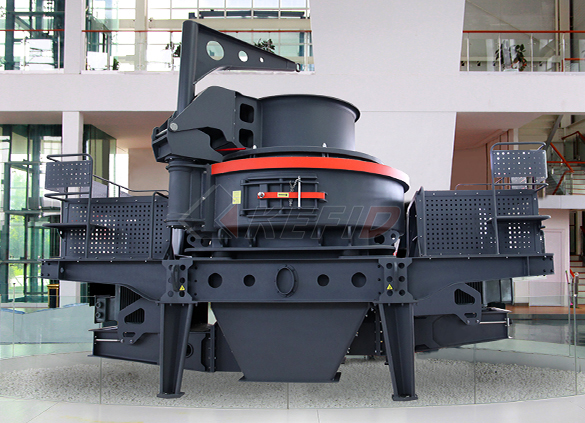

VSI6S vertical shaft impact crusher
-

Deep rotor vsi crusher
-

B series vsi crusher
-

Vertical grinding mill
-

Ultra fine vertical grinding mill
-

MTW european grinding mill
-

MB5X158 pendulum suspension grinding mill
-

Trapezium mill
-

T130X super-fine grinding mill
-

Micro powder mill
-

European hammer mill
-

Raymond mill
-
Ball mill
-

GF series feeder
-

FH heavy vibrating feeder
-

TSW series vibrating feeder
-

Vibrating feeder
-

Vibrating screen
-

S5X vibrating screen
-

Belt conveyor
-

Wheel sand washing machine
-

Screw sand washing machine
-
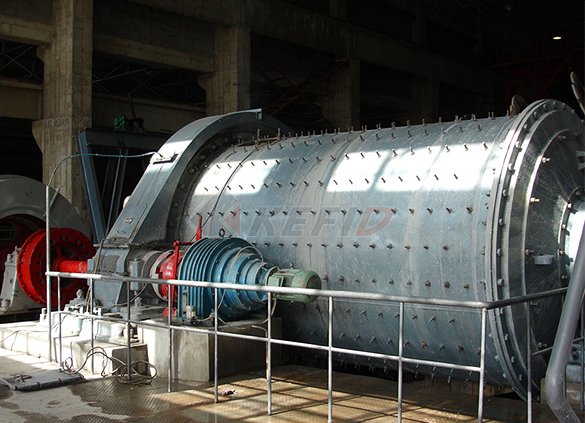

Rod mill
-
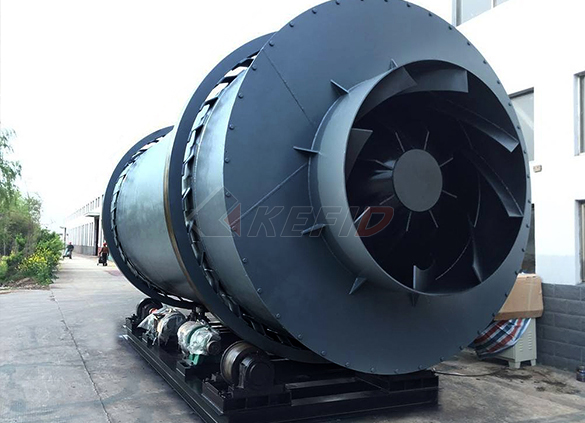

Dryer
-
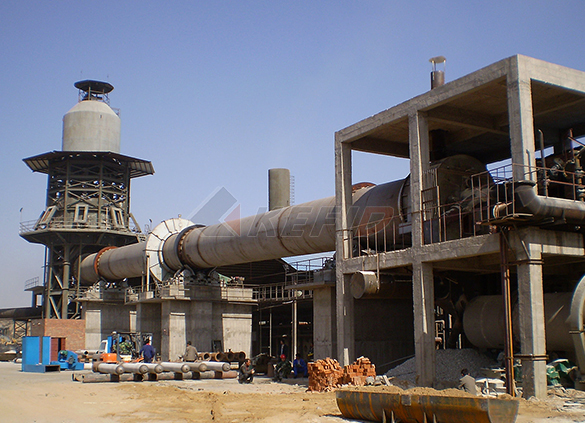

Rotary kiln
-
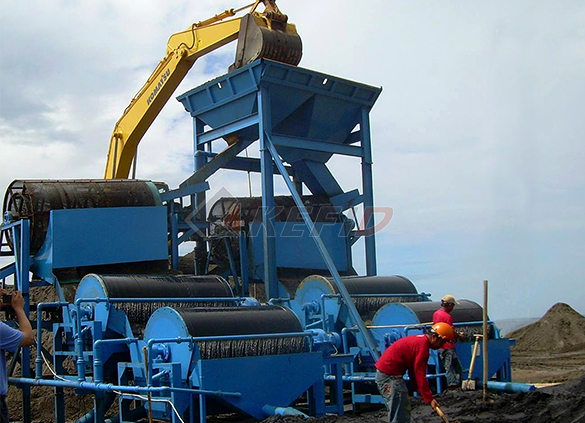

Wet magnetic separator
-

High gradient magnetic separator
-

Dry magnetic separator
-

Flotation machine
-

Electromagnetic vibrating feeder
-
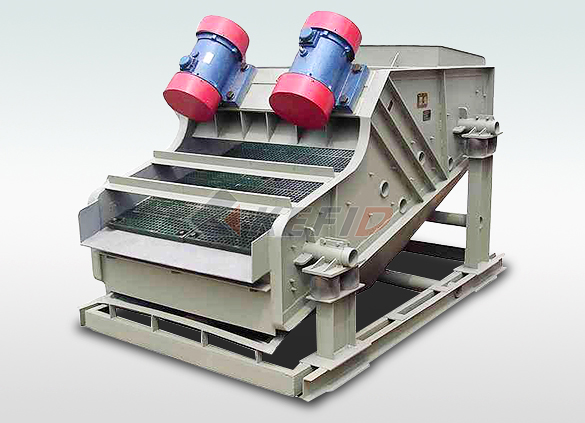

High frequency screen

Typical Road Structure Cross Section Sub Grade, Base
a Function of Sub base in Road Cross Section It enables traffic stresses to be reduced to acceptable levels in subgrade in the Road Cross Section so that excessive deformation is prevented It acts as a working plate form for the construction of upper pavement layers Acts as a drainage layer1 Subgrade is the foundation of the road, thus its the lowest and most important component of road structure 2 SUB BASE Consists of a Upper Base Courseb Sub or Lower Base Course If natural surface is above the formation level then the surface is Components of Road Structure Functions and Construction A road surface (British English), or pavement (American English), is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkwayIn the past, gravel road surfaces, cobblestone and granite setts were extensively used, but these have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base courseRoad surface WikipediaA composite pavement comprises multiple, structurally different layers of heterogeneous nature A typical example is a concrete pavement of two layers, sandwiching a brick layer A base of roller compacted concrete and surface course of bitumen is another exampleHighway Pavement: Layers, Functions, Types, Defects, Rigid Nov 14, 2018 This video shows different layers of flexible pavements in very detail wayThere are three main layers, first one is subgrade layer then subbase layer then wLayers of Road Pavement Transportation Engineering

Lifelines: History by the side of the road shows layers to
Dec 20, 2020 Lifelines: History by the side of the road shows layers to a place BY TERRY WOOTEN Poet bard Allison Batdorff Just down the highway from Sep 22, 2018 highway pavement structure, describes the road pavement layer as, subgrade or the roadway formation subbase base road surface (bituminous layer highway pavement are also classified as, 1 flexible pavement 2 rigid pavement; where the suHow many layers does a road have and what is the purpose Home / Transportation / Highway Engineering Bituminous pavements are constructed in different layers such as base course, binder course and surface course These layers are made of different materials and provides different functions to the bituminous pavementsWhat are Different Layers in a Bituminous Pavement?A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places that has been paved or otherwise improved to allow travel by foot or by some form of conveyance (including a motor vehicle, cart, bicycle, or horse) Roads consist of one or two roadways (British English: carriageways), each with one or more lanes and any associated sidewalks (British English: pavement) and road vergesRoad WikipediaA road surface (British English), or pavement (American English), is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkwayIn the past, gravel road surfaces, cobblestone and granite setts were extensively used, but these have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base courseRoad surface Wikipedia

Different Types of Roads or Classification of Roads
Jun 09, 2020 The flexible road has four layers, the outer surface layer is topped with bituminous material which is called as wearing course and an underlying subbase, base and subgrade course All these layers make the road flexible Periodic maintenance is required for flexible roads otherwise it can disintegrate easily with heavy trafficFeb 16, 2018 A layer of granular material provided in between the subgrade and the base course in a road pavement is known as subbase It is provided as an additional layer when subgrade is of poor quality It consists of a layer comparatively cheaper material like burnt clinker, natural gravel or ponents Of Road Pavement Structure Daily CivilSep 22, 2018 highway pavement structure, describes the road pavement layer as, subgrade or the roadway formation subbase base road surface (bituminous layer highway pavement are also classified as, 1 flexible pavement 2 rigid pavement; where the suHow many layers does a road have and what is the purpose Concrete road surfaces are composed from cement and other materials, such as aggregate, fly ash and chemical admixtures The concrete is laid on a prepared surface in jointed blocks, or in a continuous layer reinforced by mesh or steel This type of road surface has only occasionally been used in Different Road Construction Surfaces: Pros and Cons KH PlantA road to be built by an operator whose only equipment is a bulldozer requires a different design than a road to be built by a contractor equipped with hydraulic excavator, scrapers, and bulldozer Table 38 lists common road construction equipment and their suitability for the different phases of road constructionCHAPTER 6 ROAD CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES

(PDF) Road Construction Materials Basic Knowledge and Test
highway engineering materials Road Construction Materials Basic Knowledge and Test Procedurescomposition of the road cross section can be represented from median to lanes to curbs to daylight and a designer can simulate a wide range of road components and behaviors For example, to create an assembly for a divided highway, you begin at the baseline point and simply insert theRoad Design Basics with AutoCAD Civil and Civil 3D 2009 41 General The primary purpose of a road drainage system is to remove the water from the road and its surroundings The road drainage system consists of two parts: dewatering and drainage “Dewatering” means the removal of rainwater from the surface of the road “Drainage” on the other hand covers all the different infrastructural elements Continue reading 4 Components of road 4 Components of road drainage system ROADEX NetworkMar 24, 2015 Resurfacing is a road maintenance technique in which a new layer of asphalt is laid over the existing road surface rather than having to replace both the top and underlying base completelyThe Most Common Road Resurfacing Methods Arthur Wilson Sep 18, 2015 Swelling or shrinkage of subgrade or other layers due to moisture variation; Fig1 shows a pavement with fatigue cracking Fig1 Fatigue Cracking 2 Consolidation of Pavement Layers (Rutting) Formation of ruts falls in this type of failure A rut is a depression or groove worn into a road 10 DIFFERENT TYPES OF FAILURES OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT

Types of Pavements used in Road Construction
Two roads namely AnkapalliPudimadaka Road (AP road) – a MDR and BheemunipatnamNarsipatnam road (NB road) – a State Highway were selected for test track construction The existing width of the road pavement was about 35m and as per state PWD programme, has to be increased to 55m by 1m widening the carriageway on both sides of the roadDec 22, 2018 Hello friends, This video is regarding layers in road like Embankment, Subgrade, Blanket, GSB, Blanket, DLC/WMM, PQC/ DBM, BC,BM etc 1 Expansion joint on Major Bridges https://youtube/07UNACKYJ Road/Highway(Flexible/Rigid) Layers YouTubeAug 28, 2020 Road construction techniques were gradually improved by the study of road traffic, stone thickness, road alignment, and slope gradients, developing to use stones that were laid in a regular, compact design, and covered with smaller stones to produce a solid layer Modern roads tend to be constructed using asphalt and/or concreteRoad construction Designing Buildings WikiJun 09, 2020 The flexible road has four layers, the outer surface layer is topped with bituminous material which is called as wearing course and an underlying subbase, base and subgrade course All these layers make the road flexible Periodic maintenance is required for flexible roads otherwise it can disintegrate easily with heavy trafficDifferent Types of Roads or Classification of RoadsDepending on the stresses to be expected, the road comprises various layers of different thickness in order to withstand the most diverse weather conditions and remain serviceable for many decades the A1 highway needed a road surface designed to withstand heavy loads A 20 cm thick gravel layer serves as frost protectionConstruction of base layers Road construction

Pavement Structure Pavement Interactive
A flexible pavement structure is typically composed of several layers of material each of which receives the loads from the above layer, spreads them out, then passes them on to the layer below Thus, the further down in the pavement structure a particular layer is, the less load (in terms of force per area) it must carry (see Figure 1) Figure 1Feb 16, 2018 A layer of granular material provided in between the subgrade and the base course in a road pavement is known as subbase It is provided as an additional layer when subgrade is of poor quality It consists of a layer comparatively cheaper material like burnt clinker, natural gravel or ponents Of Road Pavement Structure Daily CivilTwo roads namely AnkapalliPudimadaka Road (AP road) – a MDR and BheemunipatnamNarsipatnam road (NB road) – a State Highway were selected for test track construction The existing width of the road pavement was about 35m and as per state PWD programme, has to be increased to 55m by 1m widening the carriageway on both sides of the roadTypes of Pavements used in Road ConstructionConcrete road surfaces are composed from cement and other materials, such as aggregate, fly ash and chemical admixtures The concrete is laid on a prepared surface in jointed blocks, or in a continuous layer reinforced by mesh or steel This type of road surface has only occasionally been used in Different Road Construction Surfaces: Pros and Cons KH Plant41 General The primary purpose of a road drainage system is to remove the water from the road and its surroundings The road drainage system consists of two parts: dewatering and drainage “Dewatering” means the removal of rainwater from the surface of the road “Drainage” on the other hand covers all the different infrastructural elements Continue reading 4 Components of road 4 Components of road drainage system ROADEX Network

Building a Great Gravel Road: 10 Basic Principles KH Plant
6 Construct in layers The best gravel roads are constructed upwards in layers from a stable base The base and binder layers should be allowed to harden and settle before the final surface layer is applied If you start with a poor base, the entire road is compromised, and no amount of top dressing or grading will rescue the situation 7Mar 24, 2015 Resurfacing is a road maintenance technique in which a new layer of asphalt is laid over the existing road surface rather than having to replace both the top and underlying base completelyThe Most Common Road Resurfacing Methods Arthur Wilson Sep 18, 2015 Swelling or shrinkage of subgrade or other layers due to moisture variation; Fig1 shows a pavement with fatigue cracking Fig1 Fatigue Cracking 2 Consolidation of Pavement Layers (Rutting) Formation of ruts falls in this type of failure A rut is a depression or groove worn into a road 10 DIFFERENT TYPES OF FAILURES OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT Mar 06, 2018 Why Camber Is Provided In Road? 1 To protect the road by preventing the entry of surface water into the subgrade soil through pavement 2 To prevent the entry of water into the bituminous pavement layers 3 To remove the rainwater from the pavement surface as quickly as possible and to allow the pavement to get dry soon after the rainTypes Of Road Camber Advantages And Methods Of Providing The thckness design of the pavement is the determination of the overall thickness of the road and the thickness of the individual layers This is of course dependant on the type of material chosen for the road This is explained in more detail below The procedure described in this page is that in the Design Manual for Roads and Bridges, Volume 7Pavement Design Thickness

CHAPTER 3 ROAD DESIGN
Table 21 lists various subgrade width for a 300 m traveled road width and different ballast depth requirements Table 21 Required subgrade width (exclusive fo fill widening) as a function of road width, ballast depth and ditch width Roadwidth = 30 m, ditch = 09 m (1:1 and 2:1 slopes), shoulderslopes 2:1Jun 06, 2017 Subgrade act as a cushion for other layers ie In order to achieve durable road subgrade should be strong Subgrade is provided by digging up the subsoil and the level of the subgrade is decided by subtracting the total thickness of the pavement from the finished level of the road pavement The subgrade is thoroughly compacted by rollers 6 BASIC STEPS COMPRISING ROAD CONSTRUCTION PROCEDURE