Solutions
Products
-
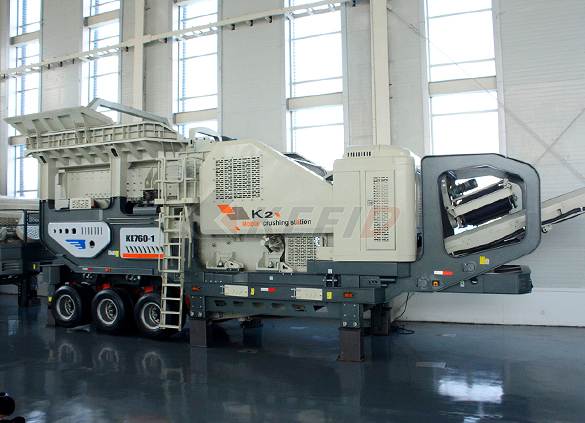

Primary mobile crushing plant
-
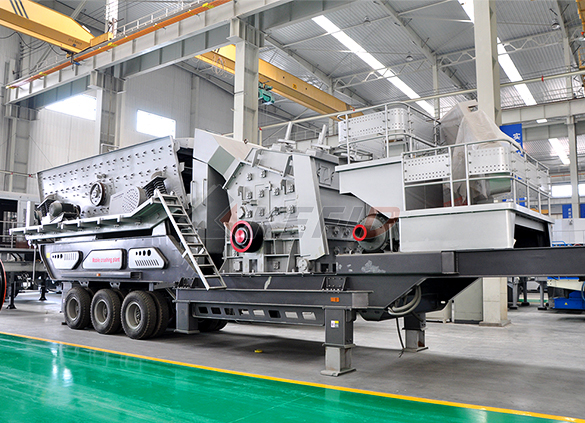

Independent operating combined mobile crushing station
-
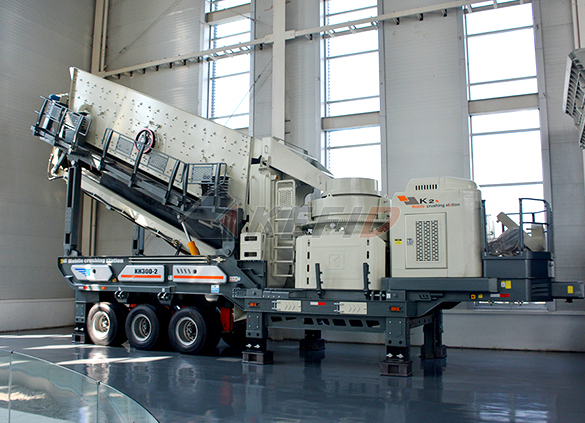

Mobile secondary crushing plant
-
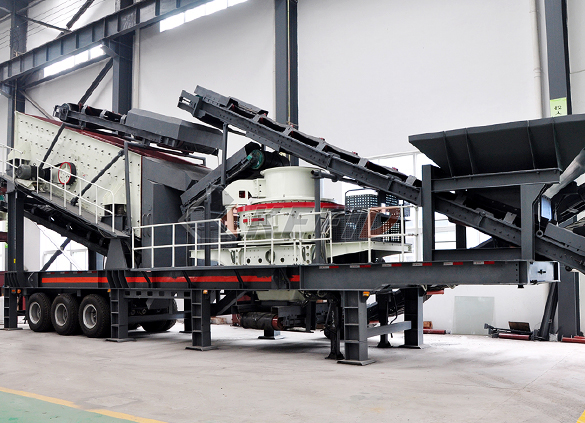

Fine crushing and screening mobile station
-
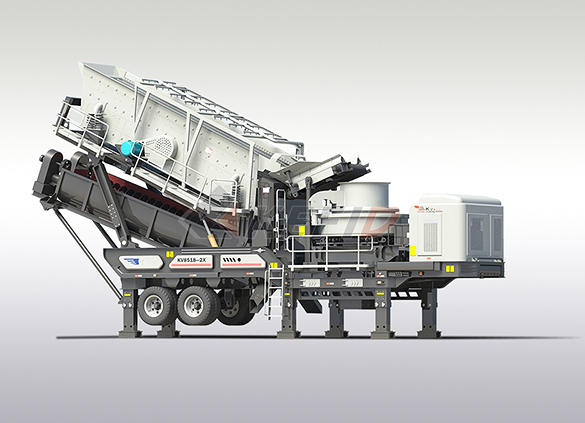

Fine crushing & washing mobile station
-
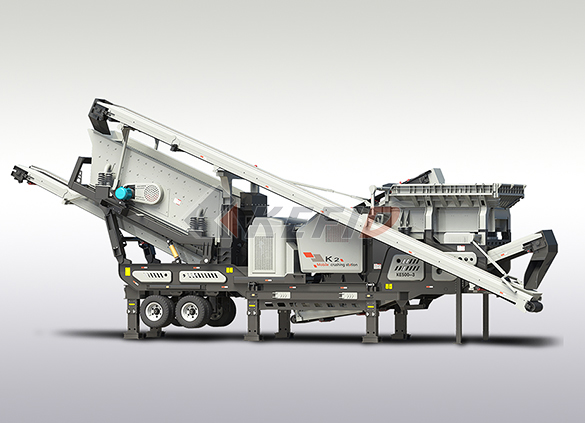

Three combinations mobile crushing plant
-
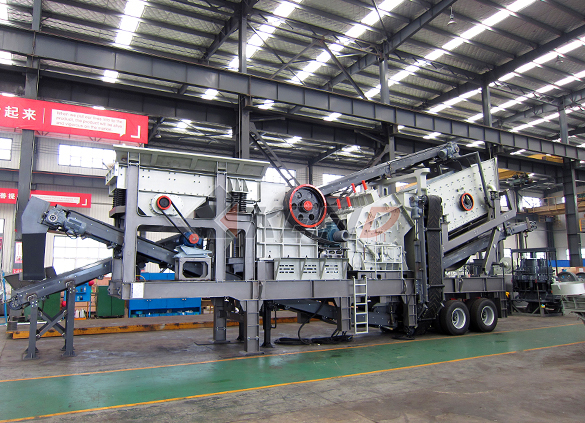

Four combinations mobile crushing plant
-
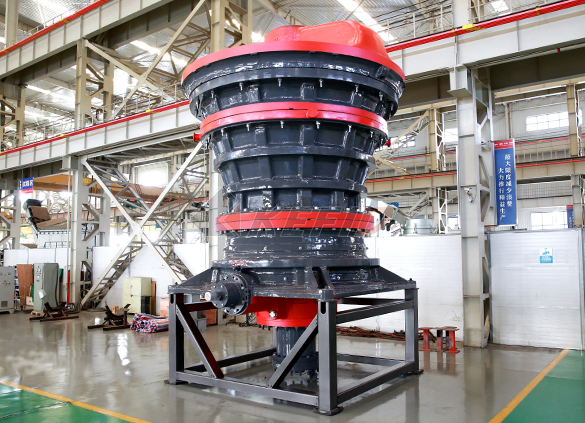

HGT gyratory crusher
-

C6X series jaw crusher
-

JC series jaw crusher
-

Jaw crusher
-

HJ series jaw crusher
-
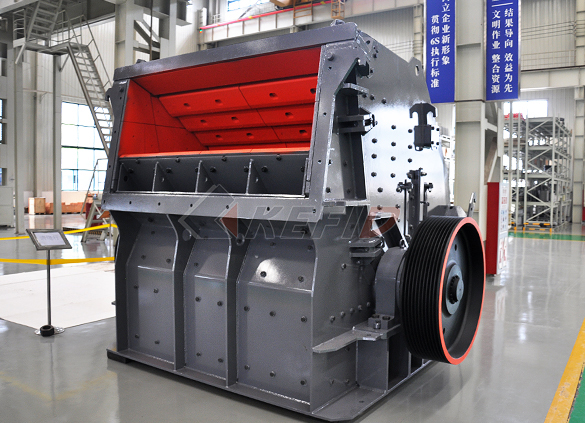

CI5X series impact crusher
-
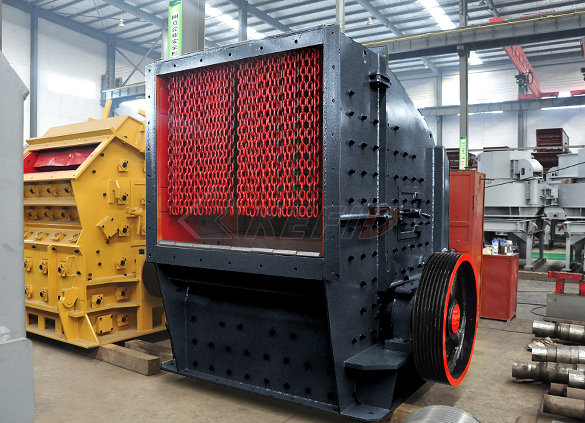

Primary impact crusher
-
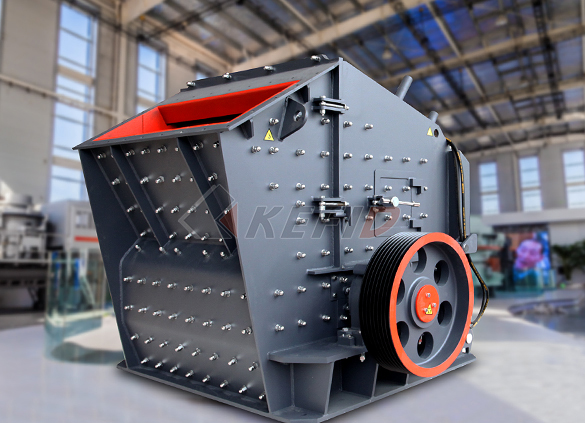

Secondary impact crusher
-
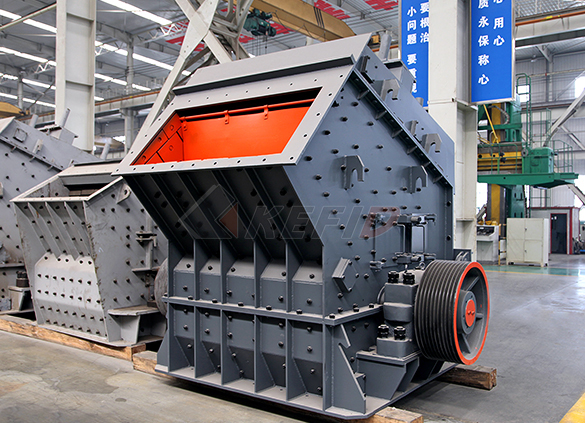

Impact crusher
-

HPT series hydraulic cone crusher
-

HST hydraulic cone crusher
-

CS cone crusher
-

VSI6S vertical shaft impact crusher
-

Deep rotor vsi crusher
-

B series vsi crusher
-

Vertical grinding mill
-

Ultra fine vertical grinding mill
-

MTW european grinding mill
-

MB5X158 pendulum suspension grinding mill
-

Trapezium mill
-

T130X super-fine grinding mill
-

Micro powder mill
-

European hammer mill
-

Raymond mill
-
Ball mill
-

GF series feeder
-
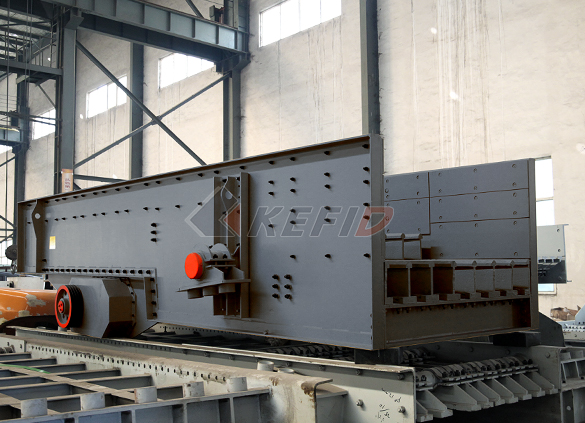

FH heavy vibrating feeder
-
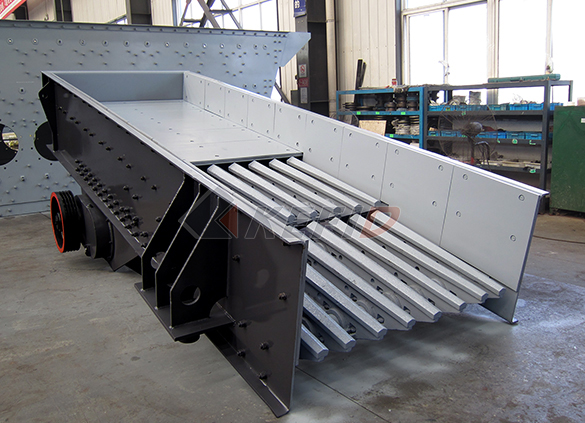

TSW series vibrating feeder
-
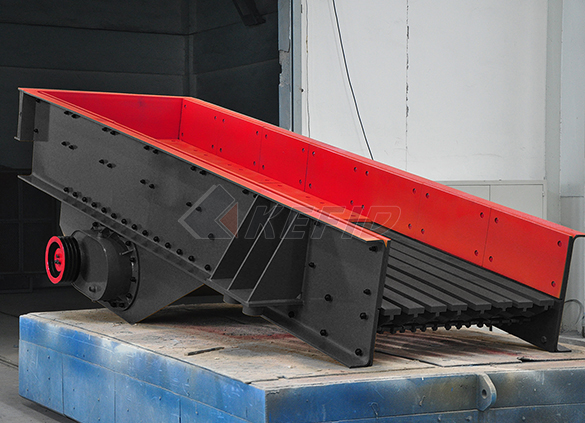

Vibrating feeder
-
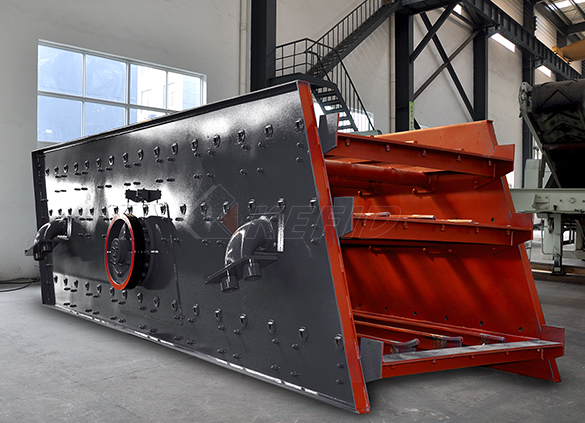

Vibrating screen
-
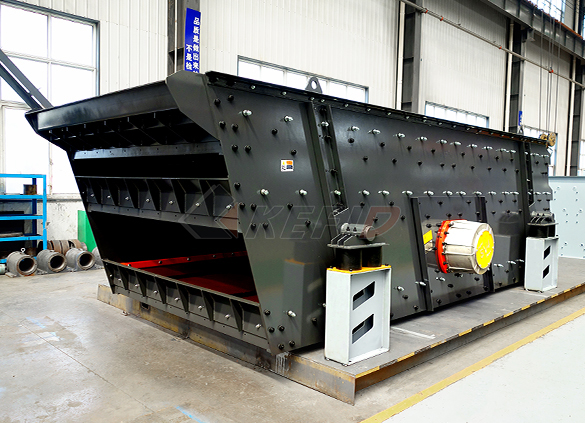

S5X vibrating screen
-
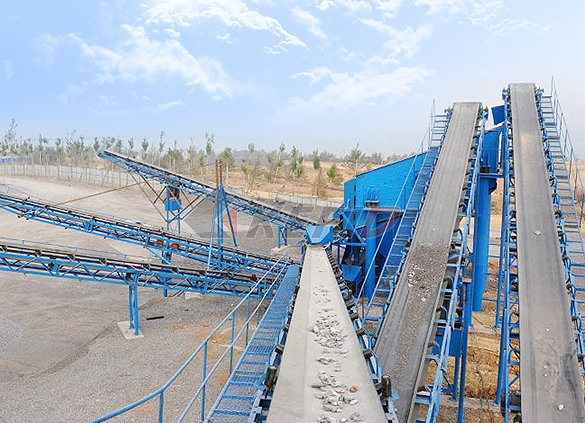

Belt conveyor
-
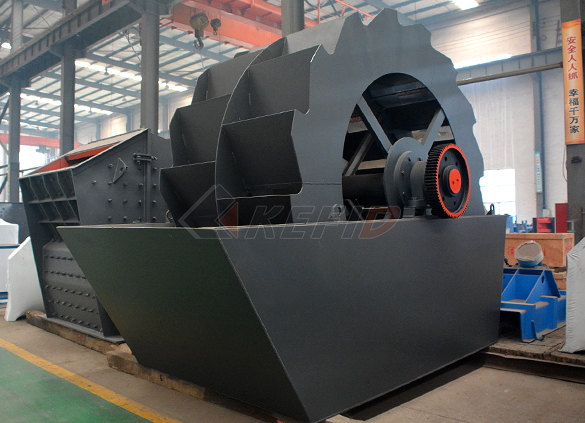

Wheel sand washing machine
-
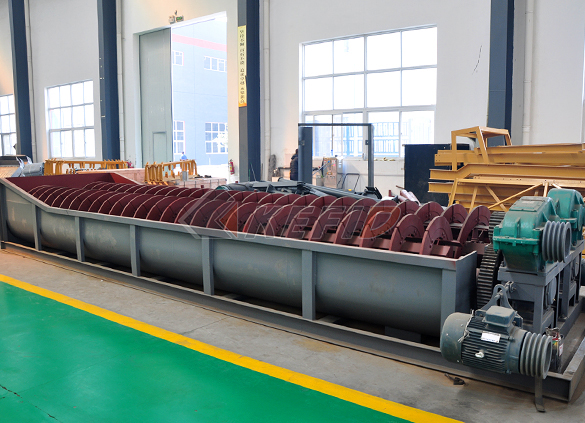

Screw sand washing machine
-
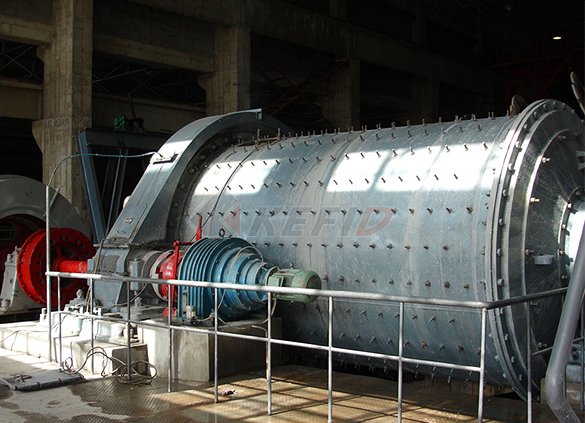

Rod mill
-
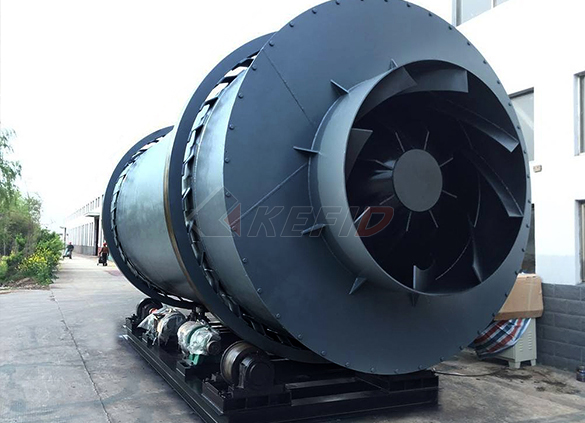

Dryer
-
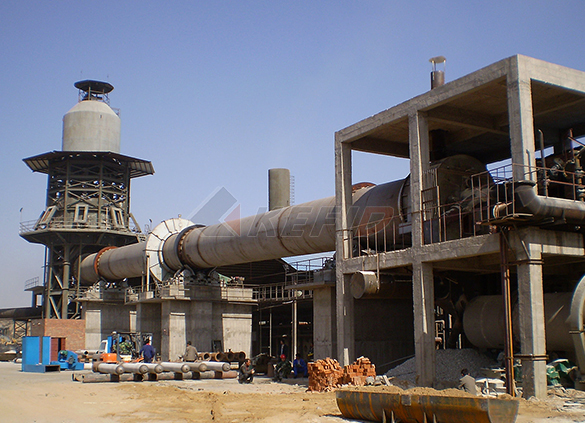

Rotary kiln
-
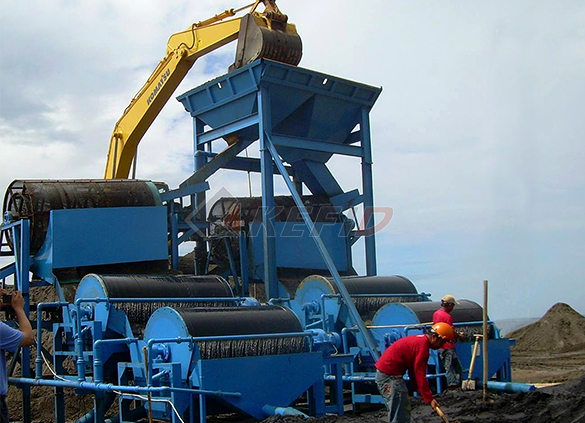

Wet magnetic separator
-
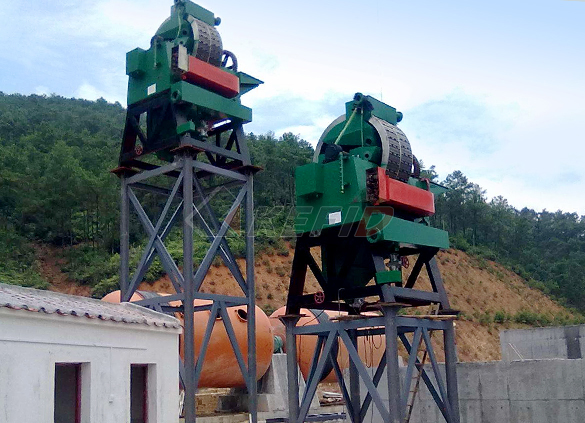

High gradient magnetic separator
-
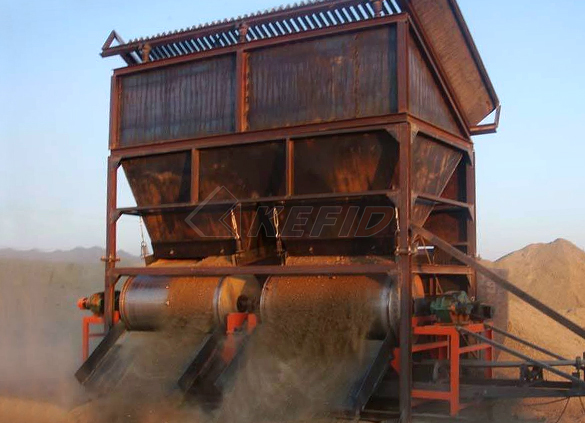

Dry magnetic separator
-
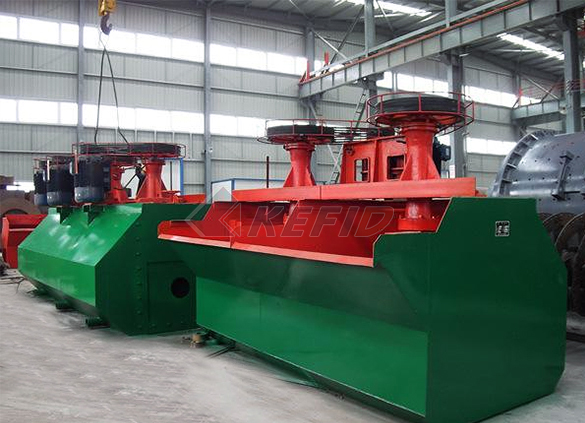

Flotation machine
-
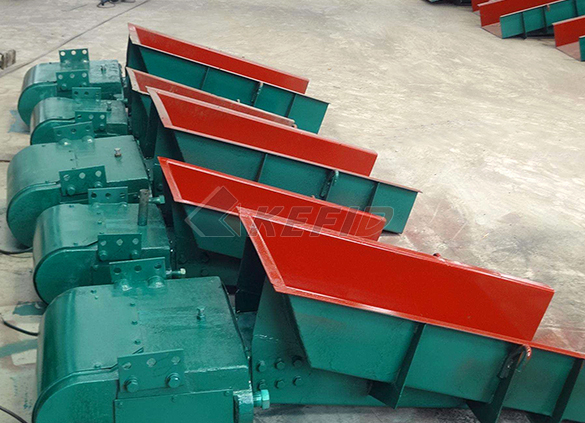

Electromagnetic vibrating feeder
-

High frequency screen

Hydrometallurgical Processes for the Recovery of Metals
Nov 13, 2020 After leaching, MnCO3and FeCO3were recovered from the solution by heating, with the NH3and CO2driven off Under optimum conditions, 80% of processes In the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese from its ore, the leach liquors often contain divalent ions such as iron, , copper, nickel, cobalt and zinc along with other manganese impurities which make manganese very difficult to separate The processes employed for soluHydrometallurgical Processing of Manganese Ores: A ReviewSep 01, 2020 In Fig 4, one can see that as the H 2 SO 4 concentration increases from 05 mol/L to 25 mol/L, the leaching percentages of manganese, iron, and copper increase, indicating that an increased H 2 SO 4 concentration is beneficial for these reactions (Equations (6), (7), (8), and (9))Hydrometallurgical recovery of manganese, gold and silver DOI: 103390/MIN Corpus ID: Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching Manganese from SemiOxidized Manganese Ores with Sucrose @article{Wang2017HydrometallurgicalPA, title={Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching Manganese from SemiOxidized Manganese Ores with Sucrose}, author={Y Wang and Shenglong [PDF] Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching The extraction of manganese from a semioxidized manganese ore was investigated with sucrose as the reducing agent in dilute sulfuric acid medium The kinetics of leaching manganese from the complex ore containing MnCO3 and MnO2 was also investigated The effects of sucrose and sulfuric acid concentrations, leaching temperature and reaction time on the total Mn (TMn), MnO2 and MnCO3 leaching Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching

A Kinetic Study of the Leaching of Iron and Manganese from
A good number of works have been reported on the hydrometallurgical leaching of iron and manganese from their ores using various leachants such as chloride media, mineral acids with or without oxidants [15] Limited reports have, however, been published on the leaching of iron and manganese from tantalitecolumbite oreSep 10, 2020 In the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese from its ore, the leach liquors often contain divalent ions such as iron, manganese, copper, nickel, cobalt and (PDF) Hydrometallurgical Processing of Manganese Ores: A Manganese pyrohydrometallurgy A pyrometallurgical pretreatment followed by hydro metallurgical processing plays an important role in the treatmentoflowgrademanganeseoresandmanganesesea nodules containing Ni, Co and Cu values as their oxides These metal oxides in the nodules often occur in the lattices of iron and manganese mineralsManganese metallurgy review Part I: Leaching of ores Among these processes, the leaching with cheap sulfur dioxide or ferrous ion is most promising and has been operated in a pilot scale The crucial issue is the purification of leach liquors and the selective recovery of copper, nickel and cobalt is often difficult from solutions containing soluble iron and manganeseManganese metallurgy review Part I: Leaching of ores The removal of iron and manganese element from the ocean multimetallic nodules acid leaching solution was discussed For being recycled, MnO2 was choosed to oxygenate Fe2+ to Fe3+ firstly(PDF) Manganese recovery from tyrrhenian nodules by

Separation of Manganese and Iron from Reductive Leaching
A hydrometallurgical route based on solvent extraction technique was investigated for selective separation of manganese from the dust Leaching of the EAFD resulted in an aqueous feed containing 4 g/L of manganese and 087 g/L iron At the next stage, extraction of manganese and iron from the leach liquor was performed usingDOI: 103390/MIN Corpus ID: Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching Manganese from SemiOxidized Manganese Ores with Sucrose @article{Wang2017HydrometallurgicalPA, title={Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching Manganese from SemiOxidized Manganese Ores with Sucrose}, author={Y Wang and [PDF] Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching A good number of works have been reported on the hydrometallurgical leaching of iron and manganese from their ores using various leachants such as chloride media, mineral acids with or without oxidants [15] Limited reports have, however, been published on the leaching of iron and manganese from tantalitecolumbite oreA Kinetic Study of the Leaching of Iron and Manganese from Hydrometallurgy is the most suitable extractive technique for the extraction and purification of manganese as compared to all other techniques including biometallurgy and pyrometallurgical processes In the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese from its ore, the leach liquors often contain divalent ions such as iron, manganese, copper, nickel, cobalt and zinc along with other Hydrometallurgical Processing of Manganese Ores: A ReviewThe leaching efficiency of ~98% was achieved at 2h leaching time, 4 g banana peel amount, 120oC leaching temperature, 5 g manganese ore amount and 15 vol% sulfuric acid concentration The phase, microstructural and chemical analyses of LGMO samples before and after leaching confirmed that a high Mn content (~18 wt%) has been successfully Hydrometallurgical leaching and Kinetic modeling of low

Hydrometallurgical Process and Kinetics of Leaching
The extraction of manganese from a semioxidized manganese ore was investigated with sucrose as the reducing agent in dilute sulfuric acid medium The kinetics of leaching manganese from the complex ore containing MnCO3 and MnO2 was also investigated The effects of sucrose and sulfuric acid concentrations, leaching temperature and reaction time on the total Mn (TMn), MnO2 and MnCO3 leaching A process for the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese containing materials, the process characterized by the combination of a manganese dioxide containing feedstock and an acidic solution to form an acidic solution to be leached, and passing a volume of sulphur dioxide gas through that leach solution as the leaching agent, whereby no sintering or roasting pretreatment step of the USB2 Hydrometallurgical processing of manganese The consumption of manganese is increasing, but huge amounts of manganese still end up in waste in hydrometallurgical processes The recovery of manganese from multimetal solutions at low concentrations may not be economical In addition, poor iron control typically prevents the production of high purity manganeseRECOVERY AND REFINING OF MANGANESE AS BYPRODUCT The carbonate preparation doesn’t use the purification of manganese leach solutions Increasing the pH and temperature values leads to increase in iron precipitation At %2 H2O2, pH 6 and 55°C, the amount of iron and manganese are 992 % and 558% respectively At pH 3 and room temperature 78% iron and 435% manganese in the solution is removedProcess Optimization For Purification Of Manganese Leach A hydrometallurgical route could be used to prevent the problem of impurity buildup The manganese slags contain high silica, but very little iron and as a result, the usual iron removal procedures associated with leaching manganese from ores are unnecessary The thirteenth International Ferroalloys CongressRECYCLING THE RECOVERY OF MANGANESE AND

WOA1 Hydrometallurgical processing of
A process for the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese containing materials, the process characterised by the combination of a manganese dioxide containing feedstock and an acidic solution to form a leach solution, and passing a volume of sulphur dioxide gas through that leach solution, whereby the levels of dithionate ion generated in the leach solution are less than about 5g/lConcept For A Hydrometallurgical Processing Of A Copper The aim of this process is to reduce the mass that has to be leached in the hydrometallurgical process 5 the inco process shown in fig 1 starts with a combined drying and reduction step which takes place at 1000 176c in a rotary kiln after this step the nodules are smelted between 176c and separated in a manganiferous slag andHydrometallurgical Process Of Iron In Some Plant PdfThis study reports preliminary feasibility investigations for utilization of the selective carbothermic reduction and smelting (SCRS) processing scheme to beneficiate lowgrade ironmanganese (FeMn) mineral deposits from MN, USA The study includes laboratoryscale demonstrations using an induction furnace and production of various products by manipulation of operational parametersSelective Carbothermic Reduction and Smelting (SCRS The Tyrrhenian micronodules, findable at low depths (200/600 m under s l) are a reasonable reserve of manganese They can be easily and cheaply recovered but do not contain valuable metals as in the case of oceanic nodules In this work a hydrometallurgical process for manganese recovery from Tyrrhenian nodules is presented The studied treatmentManganese Recovery from Tyrrhenian Nodules by A hydrometallurgical route based on solvent extraction technique was investigated for selective separation of manganese from the dust Leaching of the EAFD resulted in an aqueous feed containing 4 g/L of manganese and 087 g/L iron At the next stage, extraction of manganese and iron from the leach liquor was performed usingSeparation of Manganese and Iron from Reductive Leaching

A Kinetic Study of the Leaching of Iron and Manganese from
A good number of works have been reported on the hydrometallurgical leaching of iron and manganese from their ores using various leachants such as chloride media, mineral acids with or without oxidants [15] Limited reports have, however, been published on the leaching of iron and manganese from tantalitecolumbite oreA process for the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese containing materials, the process characterised by the combination of a manganese dioxide containing feedstock and an acidic solution to form a leach solution, and passing a volume of sulphur dioxide gas through that leach solution, whereby the levels of dithionate ion generated in the leach solution are less than about 5g/lWOA1 Hydrometallurgical processing of The leaching efficiency of ~98% was achieved at 2h leaching time, 4 g banana peel amount, 120oC leaching temperature, 5 g manganese ore amount and 15 vol% sulfuric acid concentration The phase, microstructural and chemical analyses of LGMO samples before and after leaching confirmed that a high Mn content (~18 wt%) has been successfully Hydrometallurgical leaching and Kinetic modeling of low Combined carbonate precipitation with air oxidation is a feasible method to separate iron and manganese due to the fast kinetics, good controllability and economical reagents In addition the leaching of manganese carbonate isRECOVERY AND REFINING OF MANGANESE AS BYPRODUCT A hydrometallurgical route is proposed in this paper for the selective separation of zinc and manganese from spent alkaline batteries The recycling route comprises the following steps: (1) batteries dismantling to separate the spent batteries dust from other components (iron scraps, plastic and paper), (2) grinding of the batteries dust to produce a black homogeneous powder, (3) leaching of Development of a hydrometallurgical route for the recovery

Manganese Recovery from Tyrrhenian Nodules by
The Tyrrhenian micronodules, findable at low depths (200/600 m under s l) are a reasonable reserve of manganese They can be easily and cheaply recovered but do not contain valuable metals as in the case of oceanic nodules In this work a hydrometallurgical process for manganese recovery from Tyrrhenian nodules is presented The studied treatmentThis study reports preliminary feasibility investigations for utilization of the selective carbothermic reduction and smelting (SCRS) processing scheme to beneficiate lowgrade ironmanganese (FeMn) mineral deposits from MN, USA The study includes laboratoryscale demonstrations using an induction furnace and production of various products by manipulation of operational parametersSelective Carbothermic Reduction and Smelting (SCRS A hydrometallurgical route could be used to prevent the problem of impurity buildup The manganese slags contain high silica, but very little iron and as a result, the usual iron removal procedures associated with leaching manganese from ores are unnecessaryRECYCLING THE RECOVERY OF MANGANESE AND Hydrometallurgy is concerned with the selective leaching of metallic compounds to form a solution from which the metals Hydrometallurgy originated in the 16th century, but its principal development took place in the 20th century, stimulated partly by the desire to extract gold from lowgrade oresHydrometallurgy science BritannicaIn the hydrometallurgical processing of manganese from its ore, the leach liquors often contain divalent ions such as iron, manganese, copper, nickel, cobalt and zinc along with other impurities which make manganese very difficult to separateHydrometallurgical Processing of Manganese Ores: A Review

Bioleaching of Rare Metals from Manganese Nodules by
Manganese nodules, which constitute a potential future resource of rare metals, are composed mainly of oxides of manganese and iron, with various metals such as copper, nickel, and cobalt Although physical and chemical processes have been developed for extracting the rare metals from manganese nodules, another possible process is the leaching Herein is reported a novel green process involving natural ltartaric acid leaching, developed for the sustainable recovery of Mn, Li, Co, and Ni from spent lithiumion batteries (LIBs) Operating conditions affecting the leaching efficiencies of Mn, Li, Co, and Ni, including the concentrations of ltartaric acid (C4H6O6) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), pulp density, temperature, and leaching Recovery of Lithium, Nickel, Cobalt, and Manganese from Sulphides are suitable for processing in smelters and hydrometallurgical refineries and also minimize coprecipitation of certain impurities such as iron, aluminum, and manganese Hydroxides and carbonates are most suited to hydrometallurgical refineries which could involve either ammoniacal or acid leaching to resolubilize the nickel and cobaltNICKEL AND COBALT RECOVERY FROM MESABA